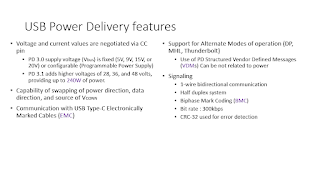
USB Power Delivery (PD) is a specification that allows devices to charge over a USB connection at higher power. Using a standard USB type C cable, it can handle up to 60W, and using an EMCA cable, it may go up to 100W ~ 240W. It operates by the power source and sink device negotiating a power contract using the USB PD protocol. In the slides, i will go through the PD protocol in details.
- Battery Charging v1.1 Spec and Adopters Agreement
- Battery Charging v1.2 Spec and Adopters Agreement
- USB 2.0 Specification
- The USB 3.2 Specification released on September 22, 2017
- USB Type-C Cable and Connector Specification Revision 2.1
- USB Power Delivery Rev 3.1
References
- USB Type-C® Cable and Connector Specification Revision 2.1
- USB Power Delivery Specification
- USB Power Delivery, Bob Dunstan, Richard Petrie – Co-charis, USB PD Group
- Wikipedia
- USB , USB-C , USB hardware
- Introduction to USB Type-C and Power Delivery, TI
- USB Type-C PD, Gregory Gosciniak, STMicroelectronics
- A primer on USB Type-C and USB Power Delivery Applications and Requirements, TI
- USB Type-C and power delivery 101 - Power delivery protocol, Embedded

















































No comments:
Post a Comment